Industrial operations that use several machines and instrumentation typically require a huge network of wires. When connecting such a large number of devices, marshalling cabinets make the job easier. In this article, we will learn more about a marshalling cabinet, review a typical layout, and compare it versus a junction box.
An Overview of the Marshalling Cabinet
In industrial applications, a marshalling cabinet provides an interface between a control system (DCS/PLC) and the field instruments. It achieves this using the marshalling technique that involves the grouping of I/O (Inputs/Outputs), which makes them easy to identify.
As a result, connecting multiple devices occurs quicker and this also simplifies maintenance. In every setup, the cabinet should contain enough terminal blocks to connect the field junction boxes to the system panels. Depending on the system, requirements could range from a few hundred to several thousand signals in the field carried by individual wire pairs, and connected to the I/O cards of the control system.
Another key function of a marshalling cabinet is cross-wiring. In large facilities, numerous digital and analogue sensors terminate into each field junction box. As a result, the signals from the cable coming into the control system may contain a mix of analogue and digital, as well as input and output signals. This hybrid situation may prove problematic for the control panel.
However, with the marshalling cabinet between both devices, its terminal blocks allow for the redirection of the signals to the appropriate module of the controller. Also, it is common to adapt different customizations to the cabinet according to a client’s specifications.
Material types vary with the planned operating environment. As an example in environments where the possibility of hydrogen blistering may occur, killed steel provides a good option with improved resistance to salt, some acids, and high temperature. Perforated steel, with its high strength-to-weight ratio, can provide ventilation and filtration for indoor mountings.
Layout
Generally, in an industrial layout, conventional cabling takes both inputs and outputs from field instrumentation to a field junction box. Then, from the junction box, a home run or multi-pair cable takes signals to a marshalling cabinet inside a control room.
Within this cabinet, cross-wiring routes each signal to its appropriate termination assembly. Finally, pre-fabricated cables connect these termination assemblies to input/output modules in the system cabinet as the figure below shows.
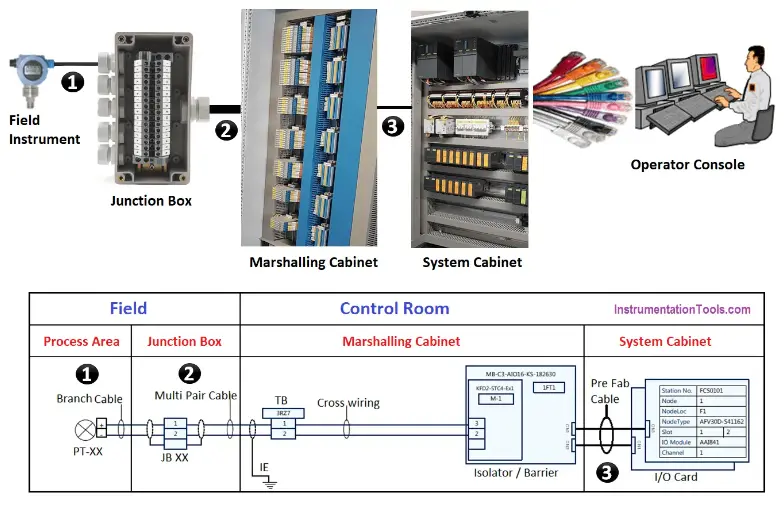
Within the marshalling cabinet, the cable routing may vary according to the type and asset specifications. However, the following are present in a typical application.
- The multi-pair cables from the junction box enter the marshalling cabinet either through a top or bottom entry.
- Then each incoming wire is terminated in the terminal block. However, if there is a requirement for surge protection, the wires are terminated in surge protection/arrester devices.
- Subsequently, cross-wiring matches the field signal to the I/O address in the termination board, for a non-IS application. In an IS application, each wire is routed to the IS barrier first, before the termination board.
- Next, the dedicated plug-and-play cables take the signal from the termination board to the I/O card in the system cabinet. Some termination boards require a dedicated DC power supply, for which marshalling cabinets typically have provision.
Marshalling Cabinet vs Junction Box
A marshalling cabinet and a junction box seemingly perform the same function because they aggregate cables from field devices. Subsequently, confusion over each type is frequent.
However, there are some fundamental differences between them as the table below highlights.
| Feature | Marshalling Cabinet | Junction Box |
| Function | Routes and organizes signals between field devices and the control system, ensuring proper I/O assignment. | Collects and consolidates field device wiring for simplified cable management. |
| Signal Management | Enables cross-wiring and signal conditioning, ensuring correct signal allocation to I/O modules. | Provides a direct connection between field devices and control panels, without internal signal redirection. |
| Components | Includes terminal blocks, IS barriers, surge protection, power distribution, and cross-wiring terminals. | Contains basic terminal blocks for wire termination, with minimal additional components. |
| Complexity | More complex, supporting multiple I/O types and system integration needs. | Simpler, mainly serving as a wiring consolidation point. |
| Application | Ideal for large-scale industrial plants requiring structured signal routing. | Suitable for basic field wiring connections in smaller setups. |

